
For example, a loan contract may state that part of a corporation’s $100,000 of retained earnings is not available for cash dividends until the loan is paid. Or a board of directors may decide to use assets resulting from net income for plant expansion rather than for cash dividends. For example, a loan contract may state that part of a corporation’s $100,000 of retained earnings is not available for cash dividends until the loan is paid. In the context of accounting, retained earnings are reported on the balance sheet under shareholders’ equity. This figure is updated periodically, typically at the end of each fiscal period, to account for the net income earned and dividends paid out during that time. Accurate tracking of retained earnings helps stakeholders understand the company’s profitability and decision-making related to profit allocation.
Company
- Retained earnings represent the portion of net income that a company chooses to reinvest in its operations rather than distribute to shareholders as dividends.
- Generally speaking, a company with a negative retained earnings balance would signal weakness because it indicates that the company has experienced losses in one or more previous years.
- Higher profitability leads to higher net income, which increases retained earnings.
- A company indicates a deficit by listing retained earnings with a negative amount in the stockholders’ equity section of the balance sheet.
- In this case, this debit balance of retained earnings will be presented as a negative in the balance sheet.
- This means that the value of the assets of the company must rise above its liabilities before the stockholders hold positive equity value in the company.
- This financial metric is crucial for understanding how a company reinvests its profits back into the business for growth and development.
In between the opening and closing balances, the current period net income/loss is added and any dividends are deducted. This helps complete the process of linking the 3 financial statements in Excel. Distribution of dividends to shareholders can be in the form of cash or stock. Cash dividends represent a cash outflow and are recorded as reductions in the cash account.
- These accounts are distinct from retained earnings, as they reflect the funds raised through equity financing rather than operational profitability.
- Though the increase in the number of shares may not impact the company’s balance sheet, it decreases the per-share valuation, which is reflected in capital accounts, thereby impacting the RE.
- It includes the beginning balance, net income, dividends paid, and the ending balance.
- However, note that the above calculation is indicative of the value created with respect to the use of retained earnings only, and it does not indicate the overall value created by the company.
- Profits give a lot of room to the business owner(s) or the company management to use the surplus money earned.
- So for example there are contra expense accounts such as purchase returns, contra revenue accounts such as sales returns and contra asset accounts such as accumulated depreciation.
Retained Earnings: How to Calculate, Manage, and Use Them
In some industries, revenue is called gross sales because the gross figure is calculated before any deductions. It involves paying out a nominal amount of dividends and retaining a good portion of the earnings, which offers a win-win. Management and shareholders may want the company to retain earnings for several different reasons. Being better informed about the market and the company’s business, the management may have a high-growth project in view, which they may perceive as a candidate for generating substantial returns in the future. Retained earnings are also called earnings surplus and represent reserve money, which is available to company management for reinvesting back into the business. When expressed as a percentage of total earnings, it is also called the retention ratio and is equal to (1 – the dividend payout ratio).
What is the Retained Earnings Formula?
The analyst prefers this statement when they perform financial statements or investment analyses related to retained earnings. Alternatively, if it is to correct the understatement of prior period net income, the company will credit the retained earnings in the journal entry instead. Retained earnings play a vital role in a company’s financial health, providing insight into its profitability, growth potential, and ability to reinvest in itself. By understanding the concepts and calculations related to retained earnings, businesses can better manage their financial resources and ensure long-term success. Whether you’re an accountant, investor, or business owner, grasping the intricacies of retained earnings is key to making informed financial decisions.
End of Period Retained Earnings
Retained earnings accumulate over time and reflect the company’s ability to generate profits and retain them for growth or other financial needs. Retained earnings, on the other hand, specifically refer to the portion of a company’s profits that remain within the business instead of being distributed to shareholders as dividends. If a company decides not to pay dividends, https://www.bookstime.com/ and instead keeps all of its profits for internal use, then the retained earnings balance increases by the full amount of net income, also called net profit. Dividend distributions also play a significant role in affecting retained earnings.
Time Value of Money
- This balance signifies that a business has generated an aggregate profit over its life.
- This usually gives companies more options to fund expansions and other initiatives without relying on high-interest loans or other debt.
- Conversely, consistently low retained earnings might raise concerns about the company’s financial performance and its ability to sustain operations.
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
- The company can make the retained earnings journal entry when it has the net income by debiting the income summary account and crediting the retained earnings account.
Although you can invest retained earnings into assets, they themselves are not assets. Changes in the composition of retained earnings reveal important information the retained earnings account normally: about a corporation to financial statement users. A separate formal statement—the statement of retained earnings—discloses such changes. Yes, having high retained earnings is considered a positive sign for a company’s financial performance. Most software offers ready-made report templates, including a statement of retained earnings, which you can customize to fit your company’s needs.


However, this creates a potential for tax avoidance, because the corporate tax rate is usually lower than the higher marginal rates online bookkeeping for some individual taxpayers. Higher income taxpayers could “park” income inside a private company instead of being paid out as a dividend and then taxed at the individual rates. To remove this tax benefit, some jurisdictions impose an “undistributed profits tax” on retained earnings of private companies, usually at the highest individual marginal tax rate.
Accounting for Restricted Retained Earnings
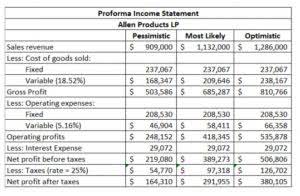
Retained earnings are not cash; they represent profits that may be tied up in assets such as inventory, equipment, or accounts receivable. And due to the business judgement rule, the board may opt not to declare dividends regularly. Examples of these items include sales revenue, cost of goods sold, depreciation, and other operating expenses.
Management and Retained Earnings

Accurate reporting of retained earnings is vital for investors and analysts who assess the company’s growth potential and financial stability. Retained earnings are a crucial component of a company’s financial health, representing the accumulated profits that a company retains rather than distributing them as dividends to shareholders. We cover key topics such as the definition of retained earnings, how they appear on a balance sheet, their impact on a company’s financial statements, and how they are calculated and managed. The amount of retained earnings that a corporation may pay as cash dividends may be less than total retained earnings for several contractual or voluntary reasons. These contractual or voluntary restrictions or limitations on retained earnings are retained earnings appropriations.