
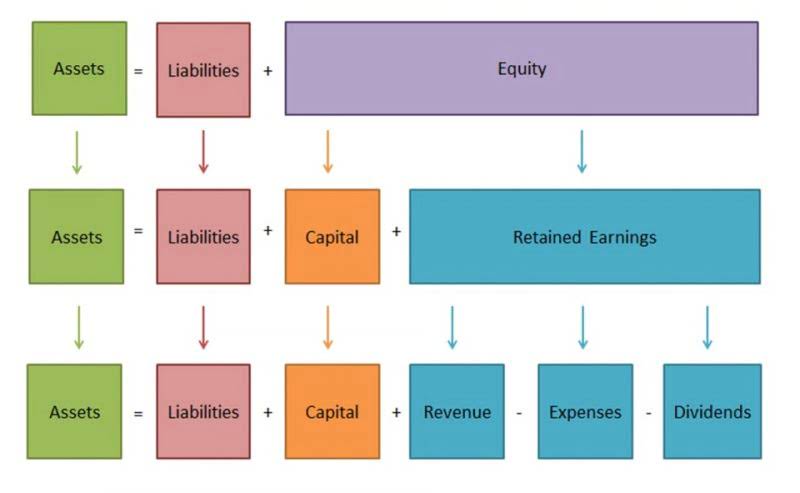
Moreover, inflation devalues the purchasing power of today’s currency as time goes on. For example, a five-dollar bill in the 1950s would not be able to purchase as much in the 2020s as it could in the 1950s. Unless the five dollars is earning interest at the rate of inflation, it will slowly become worthless over time. For instance, five dollars in 1950 is actually worth about $50 in 2015. Said a different way, a 1950 dollar is worth about 10 times a 2015 dollar. In financial accounting this term refers to the amount of debt excluding interest.
- Of course, both calculations also hinge on whether the rate of return you chose is accurate.
- It helps you find the total value of those future payments in today’s dollars.
- Once you have located this discount rate, you can multiply it by the cash amount to be received at a future date to calculate the present value of that sum.
- For investments, you might use your expected return or cost of capital.
- The higher the discount rate you select, the lower the present value will be because you are assuming that you would be able to earn a higher return on the money.
- Kristin is a Certified Public Accountant with 15 years of experience working with small business owners in all aspects of business building.
Time Value of Money Calculators
A discount rate selected from this table is then multiplied by a cash sum to be received at a future date, to arrive at its present value. The interest rate selected in the table can be based on the current amount the investor is obtaining from other investments, the corporate cost of capital, or some other measure. To record the cash equivalent amount through a present value calculation, the accountant must estimate the interest rate (i) appropriate for discounting the future amount to the present time. The rate will reflect the length of time before the money will be received as well as the credit worthiness of MedHealth, Inc. Let’s assume What is bookkeeping that the appropriate rate is 10% compounded annually.
Handling More Than One Future Amount
By being able to accurately calculate the present value of a sum, you can better understand the long-term effects of different investments. Present value, often called the discounted value, is a financial formula that calculates how much a given amount of money received on a future date is worth in today’s dollars. In other words, it computes the amount of money that must be invested today to equal the payment or amount of cash received on a future date. We need to calculate the present value (the value at time period 0) of receiving a single amount of $1,000 in 20 years. The interest rate for discounting the future amount is estimated at 10% per year compounded annually. Because the PV of 1 table had the factors rounded to three decimal places, the answer ($85.70) differs slightly from the amount calculated using the PV formula ($85.73).

Types of Present Value Tables
Present value tables make this process way easier, especially when modeling multiple interest rate scenarios. If you’re trying to make smart and future-facing money decisions, chances are this table belongs on your desk (or spreadsheet). Need to know what $10,000 five years from now is worth at 7%?
Present Value Tables
Behind every table, calculator, and piece of software, are the mathematical formulas needed to compute present value amounts, interest rates, the number of periods, and the future value amounts. We will, at the outset, show you several examples of how to use the present value formula in addition to using the PV tables. The Ordinary Annuity table already accounts for the fact that 20 payments will be made. Therefore, when we do the calculation, we only need to multiply the factor by a single interest payment. When evaluating investments, we typically look at rate of return.
In year two the account balance will earn $63.60 (not $60.00) because 6% interest is earned on $1,060. Similarly the bank paying the interest will incur interest on interest. For example, instead of paying $100 cash a person is allowed to pay $9 per month for 12 months. The interest rate is not stated, but the implicit rate can be determined by use of present value factors. As you have seen, the frequency of compounding requires you to adjust the number of periods (n).

The PV tables are available for download in PDF format by following the link below.
Present Value of a Single Sum of Money
Payments on mortgage loans usually require monthly payments present value of single sum table of principal and interest. This tells us that the missing component, the interest rate (i), is approximately 1% per month. However, the exercise asked for the annual interest rate, compounded monthly. The annual interest rate is approximately 12% (the approximate monthly interest rate x 12 months).
Present value tables list present value factor for multiple interest rates and time periods. The answer tells us that receiving $10,000 five years from today is the equivalent of receiving $7,440.90 today, if the time value of money has an annual rate of 6% compounded semiannually. You are purchasing the right to receive $20,000 in 10 years when the bond matures. We need to calculate how much that is worth in today’s dollars by calculating the present value of the lump sum payment. A mentioned, the discount rate is the rate of Accounting Security return you use in the present value calculation.